Picture: Shutterstock
B vitamins support our body to convert food (carbohydrates) into energy (glucose). It 'important for pregnant woman to include all the B vitamins, known as vitamin B complex, in his diet, in that they are soluble in water and are not stored by the body. These vitamins help the mother to get adequate nutrition and support the growth and development of the child. Momjunction they say the importance and the need of all these eight B vitamins
1. Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
Image: Shutterstock
Vitamin B1, also known as thiamin or thiamin, performs many important functions during pregnancy.
- It allows you and your child to convert carbohydrates into energy.
- plays an important role in. the baby's brain development
- helps the muscles, nervous system and heart function normally
[Read: benefits of vitamin C during pregnancy ]
How Much Do You Need?
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) of vitamin B1 during pregnancy is 1.4 milligrams (mg) regardless of the age of a woman (1). Women carrying more than one baby should increase their intake of thiamine
vitamin B1 sources :.
Thiamine is found in several foods. whole grain products, cereals, fortified bread, pasta, peas, dry beans, some fish, and pork are good sources. Dairy products, fruits and vegetables also contain vitamin B1, but in small quantities (2)
Take a look at the amount of vitamin B1 present in each one of these foods :.
- ° 3/4 cup of whole grain cereal - 1.5 mg
- 1 cup of white rice (cooked) - 1.2mg
- 1 cup of rice (cooked) - 0.2 mg
- 1/2 cup oats - 0.6mg
- 1/4 cup of pecans - 0.4 mg
- 1/4 nuts Brazil - 0.4 mg
- 1/2 cup of peas (cooked) - 0.2 mg
- lentils 1/2 cup (cooked) - 0.2 mg
- 1/4 cup of wheat germ - 0.5 mg
- 1/2 cup of split peas (cooked) - 0.2 mg
- 1 cup of spinach noodles (enriched) - 0.4 mg
- 3 oz rainbow trout - 0.3 mg
- 3 ounces of salmon - 0.3 mg
- 3 ounces ham steak (boneless cured) - 0.3 mg
- 3 ounces Florida Pompano - 0.7 mg
- 3 ounces pork tenderloin - 0.8 mg
What happens if you do?. do not have enough vitamin B1
first signs of vitamin B1 deficiency include nausea, fatigue, nerve damage and headaches
A severe deficiency leads to beriberi - wet , dry or brain depending on the part of the body affects. beri-beri wet is an acute form that causes poor blood circulation and edema, which leads to heart failure. The dry form of the disease causes progressive degeneration of the nerves of the arms and legs, loss of reflexes and muscle atrophy.
[Leggi: vitamin E during pregnancy ]
Thiamine deficiency is common in developing countries, where people eat milled rice . Thiamine present in the outer coating of rice is removed during processing.
In industrial countries, alcohol is the main reason for the vitamin B1 deficiency which adversely affect the absorption of thiamine in the body.
In developed countries like the United States, foods are usually fortified with vitamin B1 , and even multivitamins and prenatal vitamins contain. Therefore, the deficiencies are rare.
Do You need a supplement?
According to the Department of Health, you can get the necessary vitamin B1 from foods such as whole grains and fortified cereals, and a balanced diet. In case you, you can not take a multivitamin or prenatal supplement to get your RDA.
What happens if you take too much?
There is no evidence to prove the negative effects of excess intake of thiamine during pregnancy.
2. Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin):
Image: Shutterstock
Vitamin B2, also known as riboflavin, is a co-enzyme which involves in many reactions in the body.
- plays a leading role in promoting healthy skin, good vision, growth and development of the child's muscles, bone., And the nerve
- will lower the risk of preeclampsia, which is a complication of pregnancy
[Read: the benefits of prenatal vitamins ].
How much do you need?
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) of vitamin B2 during pregnancy is 1.4mg. (3)
sources of vitamin B2: ..
milk, fortified cereals, wheat flour and bread products are all excellent sources of vitamin B2
Take a look the amount of riboflavin present in each of the following foods:
- 1 cup non-fat milk - 0.5 mg
- 1 cup of low-fat yogurt (plain) - 0.5 mg
- 1 1/2 ounces cheddar cheese - 0.2 mg
- 1/2 cup low-fat cottage cheese - 0.2 mg
- 1/2 cup of cottage cheese ( 1%) - 0.2 mg
- 1/2 cup mushrooms - 0.2 mg
- 1/2 cup soy - 0,3 mg
- 3 ounces of pork spare ribs (offers) - 0.3 mg
- 1/2 cup of spinach (cooked) - 0.2 mg
- 3 ounces tempeh (cooked) - 0.3 mg
- 1 boiled egg (large) - 0.3 mg
- 3 ounces skinless duck - 0.4 mg
- 1/4 cup almonds - 0.3 mg
Attention: UV light can destroy riboflavin in foods, so these foods should be stored in opaque containers away from light.
What happens if you do not have enough vitamin B2?
The signs of riboflavin deficiency are skin rash, anemia, dermatitis, magenta (red and dry) of the tongue, cracking and dryness around the lips, mouth and nose.
You are at a higher risk of deficiency, if you are suffering from anorexia (eating disorders) and lactose intolerance (because you want to be avoiding dairy products)
[Read: vitamin K during pregnancy ].?
Do you need a supplement
The Department of Health says that you can get the necessary riboflavin through a healthy diet that contains multi-grains, eggs, meat, dairy products, green vegetables and fortified cereals. If you use supplements, do not take them beyond the recommended daily limit.
What happens if you take too much?
There is no evidence about the negative effects of excess intake of vitamin B2. Each vitamin B2 that is not used by the body is usually excreted in the urine.
3. Vitamin B3 (Niacin):
Image: Shutterstock
Vitamin B3, also called niacin, is present in two forms -. nicotinamide and nicotinic acid, both of which help to release energy from food
- It keeps the skin, the nervous system and healthy mucous membranes [
- and 'essential for brain development of child.
- helps relieve nausea, lower a painful migraine, and improves digestion.
niacin is filed under pregnancy category C by the US FDA. Studies have revealed that it can cause damage in animals, but more research is needed to learn about its effect on human beings
. [Read: Why do pregnant women need magnesium ]
How much do you need?
The recommended amount of vitamin B3 during pregnancy is 18mg per day (4). You can include up to 35 mg per day, and intake of vitamin B3 between these two levels is acceptable during pregnancy. . According to Merck Manuals Medical Library, 'intake of more than 35 mg has not been studied in pregnant women', so it is not advisable
sources of vitamin B3 :.
Both nicotinamide and nicotinic acid found in food. You can include the following foods to get the amount of niacin needed:
- 4 oz chicken breast (roasted) - 14.41mg
- 4 oz salmon (grilled or baked) - 11.34mg
- 4 oz yellow or tuna (grilled or baked) - 13.54mg
- 4 oz Turkey - 8.50mg
- 4 oz veal liver (fried) - 9.61mg
- 4 oz deer - 7.61mg
- 4 oz Halibut (grilled or baked) - 8.08mg
- 5 oz crimini mushrooms (raw) - 5:39 mg
- 4 oz lamb loin (roasted) - 7.75mg
What happens if you do not have enough vitamin B3
deficiency of vitamin B3 is as rare as you It will be easy to get the daily requirement from? food sources or available from tryptophan (an amino acid, which makes niacin) present in food proteins (5). The deficit is usually higher in those who consume corn or sorghum as a staple food. Niacin is present in bound form in these sources.
Do you need a supplement?
The supplementation is usually not necessary as you get enough vitamin B3 in an average diet.
What happens if you take too much?
There are no adequate studies to determine the effects of vitamin B3 taken in high doses during pregnancy. They are otherwise known to cause flushing of the skin and liver damage.
oral niacin is classified in category C pregnancy by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the drug is not fully been studied in pregnant women. Since there is no adequate evidence to determine its effects on the mother and the fetus, the drug should be taken with caution
[Read: Vitamin D during pregnancy ].
FDA has approved the use of niacin in therapeutic doses lowers triglycerides and cholesterol. But the dosage is 6g, which is much higher than the dose recommended during pregnancy. Therefore, you should stop taking niacin during pregnancy, especially when you are taking for low HDL cholesterol or high LDL. But, if you are taking to high triglycerides, you should take notice of the doctor as elevated triglycerides during pregnancy.
4. Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid):
Image: Shutterstock
Vitamin B5 or pantothenic acid is a component of CoA reductase (coenzyme a), essential for various chemical reactions in the cells.
- helps prevent muscle cramps during pregnancy.
- releases hormones that help fight stress.
- and 'useful for the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates and fats.
How much do you need?
your body requires 6 mg of pantothenic acid per day during pregnancy (6)
sources of vitamin B5 :.
Pantothenic acid is found in almost all varieties of meat and vegetables. Here are some good options to get the required amount of this vitamin:
- 1/4 cup sunflower seeds (dry roasted) - 2.3mg
- 3/4 cup of whole grain cereal (fortified) - 10mg
- 8 ounces low-fat yogurt (plain) - 1.3 mg
- 5 ounces crimini mushrooms (raw) - 2.1 mg
- 1 baked sweet potato (medium-sized) - 1mg
- 1/2 avocado (medium-sized) - 1.1mg
- 1/2 cup yellow corn (cooked) - 0.7 mg
- 1 cup non-fat milk - 1mg
- 1 potato (baked) - 0.7 mg
- 1/2 cup of chocolate chips assorted seeds and salted nuts - 0.7 mg
- 1 cup of oatmeal (cooked) - 0.5 mg
- 1/2 cup mushrooms (raw) - 0, 5 mg
- 1 orange (medium) - 0.5 mg
- 1 banana (medium) - 0.5 mg
- 1/2 cup of cauliflower (boiled) - 0.3 mg
- 1/2 cup of broccoli (boiled) - 0.3 mg
- 1 boiled egg (large) - 0.7 mg
- 3 ounces chicken breast (roasted) - 1mg
- 3 ounces salmon (baked) - 1.2mg
What happens if you do not have enough vitamin B5?
B5 deficiencyThe vitamin is rare when you are pregnant. There is a risk of its deficiency in women who are severely malnourished, or on a diet or suffering from toxemia (an abnormal condition during pregnancy) (7). Symptoms include weakness and chronic fatigue.
Do you need a supplement?
The pantothenic acid is present in nearly all foods, and therefore do not need any additional intake. It 'also present in most of prenatal vitamin supplements.
What happens if you take too much?
Because pantothenic acid is a water soluble vitamin, the body gets rid of the excess amount through urine. The effects are not known if taken in larger amounts than the recommended dose. However, avoid excessive consumption.
5. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine):
Image: Shutterstock
vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, is essential for your body to metabolize carbohydrates, proteins and fats. It helps form red blood cells, neurotransmitters and antibodies.
- And 'essential for the development of the baby's brain and nervous system.
- it helps relieve morning sickness and maintains healthy blood glucose levels.
- prevents low birth weight in infants (8).
How much do you need?
According to the US Institute of Medicine, the daily requirement of vitamin B6 during pregnancy is 1.9mg (9). However, the maximum tolerable intake is 100mg for women around and above 19 years and 80 mg for those around and under 18 years old
sources of vitamin B6.
pyridoxine is located in a variety of foods. lean meat, fish, beans, and nuts are excellent sources of this vitamin. fortified cereals and breads are also good sources. Some good options are:
- 1/2 cup chickpeas (canned) - 0.57mg
- 1 baked potato (medium skin) - 0.74mg
- 1 cup spinach (cooked) - 0.44mg
- than 8 ounces of prune juice - 0.56mg
- 1 banana (medium) - 0.43mg
- 1/2 avocado - 0.26mg
- 1 cup of brown rice (long grain, cooked) - 0.28mg
- 1 ounce nuts (dry roasted) - 0.18mg
- sunflower seeds 1 oz (dry roasted) - 0.23mg
- three ounces chicken (roasted) - 0.46mg
- 3 ounces of lean pork loin (grilled) - 0.49mg
- 3 ounces farmed salmon (cooked) - 0.55 mg
what happens if you do not have enough vitamin B6?
minor deficiencies are common, while the serious deficiencies are rare. The first signs of pyridoxine deficiency include depression, sores or mouth ulcers and inflammation of the tongue.
B6 deficiencyThe vitamin can cause a form of anemia, which is similar to iron deficiency. It also reduces the production of antibodies and affects the immune response.
Do you need a supplement?
According to the Department of Health, you can get the required amount of this vitamin from a balanced diet. Most prenatal vitamin and mineral supplements contain almost 100% of the RDA
. Warning: If you have morning sickness, you should check with your doctor before taking any supplements as too pyridoxine is not safe for you and your growing fetus.
What happens if you take too much?
some multivitamins high power, that you take during pregnancy, contain pyridoxine in excess amounts. You can also get a large amount of this vitamin if you include fortified foods in your diet. Excess intake of vitamin B6 can lead to nerve damage and numbness.
6. Vitamin B7 (biotin):
Image: Shutterstock
vitamin B7 or biotin or vitamin H generates energy from the food you eat. E ', therefore, necessary to form enzymes that degrade carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
- And 'essential for embryonic growth during pregnancy.
- E 'useful for the treatment of skin rash, brittle nails and hair loss.
what you need?
As for the Food and Nutrition Board of the National Academy of Science Institute of Medicine, the recommended daily dose of vitamin B7 United States during pregnancy is 30mg (10)
[Read: biotin during pregnancy ].
sources of vitamin B7:
The bacteria that live in your digestive tract is responsible for producing some of your essential biotins. Rich food sources of biotin include egg yolk, liver, milk, oats, beets, mushrooms, salmon, pork, cheese, raspberries, cauliflower and molasses.
What happens if you do not have enough vitamin B7?
The research states that biotin is rapidly decomposed during pregnancy and then its decline in nutritional status (11). And 'it is known to cause birth defects in many animal species. Almost a third of pregnant women develop marginal biotin deficiency and indirectly shows that it can cause birth defects in the fetus (12). To exclude the risk of abnormal embryo or fetus, you must make sure that you take enough biotin during pregnancy.
The symptoms of vitamin B7 deficiency include thinning hair, depression, apathy, hallucinations and tingling in the arms and legs.
Do you need a supplement?
Pregnant women are advised to take prenatal vitamins or multivitamins that include extra biotin to help prevent birth defects.
What happens if you take too much?
Taking excess doses of biotin for a long period may lead to some side effects during pregnancy. Usually they include allergies, miscarriage and acne. However, they are rare. So, consult your doctor for the right dosage.
In addition, when you notice symptoms of allergic or acne, you should start cutting down the dosage to less than 250mg per day.
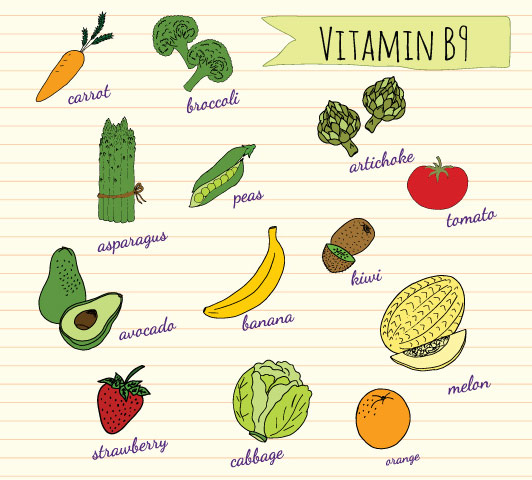
7. Vitamin B9 (folic acid):
Image: Shutterstock
vitamin B9 or folic acid is the most important vitamin B to include during pregnancy.
- prevents neural tube defects (NTDs), serious birth complications of the brain (such as anencephaly) and spinal cord (such as spina bifida). The neural tube is a section of an embryo from which the brain and the spine of the child develop.
- DTN develop in a very early stage, even before you do not know about your concept. Therefore, it is important to take folic acid supplements for some time trying to conceive.
- According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), women should take recommended amount of folic acid a month before conception and during the first trimester to reduce the risk of neural tube defects in their children by 70% (13).
- It also reduces the risk of other defects such as cleft palate, cleft palate and some heart defects in infants and preeclampsia in pregnant women.
- and 'essential for the production of red blood cells to prevent a form of anemia.
- and 'important for the synthesis of DNA, the growth of the placenta and the developing baby.
How much do you need?
The recommended daily dose of vitamin B9 is 400 mg during pregnancy (14). If you are on or prenatal multivitamins, check whether you are getting the required amount. According to WebMD, here is the amount of folic acid during pregnancy can include:
- When trying to conceive - 400mg per day
- First Quarter - 400 mg per day
- four to nine months of pregnancy -. micrograms 0mg per day
According to the National Institutes of Health, it is advisable to include at least 0mg a day during pregnancy (15)
most prenatal vitamins contain folic acid 800- 1,000mg. It is advisable not to insert more than 1,000 mg per day unless your doctor says so.
When you need extra vitamin B9?
- If you overweight , you should check with your doctor before trying to get pregnant. You may be advised to include more than 400 mg a day.
- If you pregnant with a child has NTD , your doctor may recommend include 4,000mg a day.
- If you have twins , you may be advised to include about 1,000 mg per day
E 'can also request more folic acid in the following cases :.
- A genetic mutation called methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase makes it difficult for the production of folate and folic acid in the body.
- If you are taking diabetes or AEDs.
There will be nearly 3-5% chance of having a pregnancy with NTD, so you should always talk to your doctor before trying to conceive
sources of vitamin B9: .
Folic acid is rich in lentils, dark green vegetables, sprouts, citrus fruits, asparagus, avocados, dried beans, peas and nuts. Some common food options which may include:
- 3 / 4th cup fortified cereal - 400 micrograms (mcg)
- 3 ounces beef liver (cooked and braised) - 215mcg
- lentils 1/2 cup (cooked) - 179mcg
- 1/2 egg cup noodles (enriched, cooked) - 110mcg
- 1/2 cup of spinach (cooked) - 115mcg
- 1/2 cup of great northern beans (boiled) - 0mcg
What happens if you do not have enough vitamin B9
If you are deficient in folic acid , it's true? experience the anemia, diarrhea, Loos weight, loss of appetite, sore tongue, weakness, palpitations, irritability and headaches.
If the deficiency is mild, you do not notice any symptoms, but can not get enough amounts to support the early embryonic development of the child.
Do you need a supplement?
Yes, many groups including the March of Dimes, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and the US Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all women can or planning to become pregnant should take a supplement everyday containing 400mcg of 800mcg (0.4 to 0.8 mg) of folic acid (16).
What happens if you take too much?
E 'unusual to get an overdose of folic acid. You should not take in excess of the daily limit, unless your doctor advises you to do so.
The excessive folic acid consumption may hide signs of vitamin B12 deficiency, which leads to damage to the nervous system (vitamin B12 works closely with vitamin B9). But, it is quite rare among women who are able to get pregnant.
Additionally, studies published in Journal of Endocrinology explore that an overdose of folic acid during pregnancy can put your daughters at higher risk of diabetes and obesity later in life (17 ).
9. Vitamin B12 (cobalamin):
Image: Shutterstock
Vitamin B12, also called cobalamin, has several important functions such as folic acid.
- and 'essential for the synthesis of fatty acids and myelin, which help to maintain normal neurological function and the central nervous system (CNS).
- helps in the functioning and development of blood cells, brain and nerves.
- It helps to metabolize carbohydrates, proteins and fats and so improves your mood, energy levels and levels of stress when transporting.
- Together with folate, it works for the production of red blood cells and the synthesis of DNA.
- also plays an important role in the development of the fetal brain and the formation of the neural tube.
How much do you need?
The recommended daily dose of vitamin B12 is 2.6mcg during pregnancy (18). The intake of vitamin B12 with folic acid is effective
sources of vitamin B12 :.
cobalamin is found in milk, eggs, meat, fish, poultry and seafood. Some of the best food options include:
- 4 oz snapper (baked or grilled) - 41.39mcg
- 3.25 oz sardines - 8.22mcg
- 4 ounces salmon (baked or grilled) - 3.25mcg
- 4oz scallops (baked or grilled) - 2mcg
- 4 ounces shrimp (streaming or boiled) - 1.69mcg
- 4 oz Halibut - 1.55mcg
- four ounces of venison - 3.6mcg
- four ounces of veal liver (braised) - 41.39mcg
- four ounces lamb loin (roasted) - 2.45mcg
- 4 oz lean beef (grilled) - 2.92mcg
vegans may include B12 fortified foods such as soy milk and soy products meet their daily needs. Some results of the study of the United States by Tucker, Rich et al 00 conclude that vitamin B12 fortified foods are better absorbed than vitamin B12 found naturally in foods. fortified foods using crystalline B12 or cyanocobalamin that are absorbed better.
What happens if you do not have enough vitamin B12?
vitamin B12 deficiencies are very rare among women of childbearing age. But, if they occur, increase the risk of your child being DTN development.








0 Response to "24 Vitamin B rich foods you should include in your diet during pregnancy"
Post a Comment